The National Statistical Office recently released the annual report of Periodic Labour Force Surveys conducted between July 2020 and June 2021 to estimate key employment and unemployment indicators.
New Delhi: The coronavirus pandemic has impacted the job industry with changing patterns being observed in employment rates and labour workforce participation in the country. The National Statistical Office (NSO) recently released an annual report of the Periodic Labour Force Surveys (PLFS) conducted during July 2020-June 2021, based on the data collected through the year to estimate the key employment and unemployment indicators such as worker-population ratio, labour force participation rate, unemployment rate every quarter.
The annual reports of PLFS corresponding to the periods of July 2017 to June 2018, July 2018 to June 2019, and July 2019 - June 2020 were released earlier this year.
As compared to the PLFS survey of July 2019 to June 2020, the overall labour force participation rate for all ages has increased by 1.5% and WPR has increased by a minor 1.6% in the latest report. The increase indicates that the Covid impact in labour force participation has slowly recovered. The key sectors with labour force participation for pre- and post-Covid times remains the same, with agriculture leading in rural areas, and trade, hotels and restaurants sector leading in urban areas.
Here are some key findings of the report, which covers the employment rate, industry-wise workforce participation, average incomes figure and some facts about the employment status in India.
Source of Income
India still remains a self-employed country with the majority of households in both urban and rural areas engaged as self-employed workers and casual labour. The system follows the Usual Status (Principal Status + Subsidiary Status) approach for labour force data.
Labour Force Participation Rate
The labour force participation rate in India remains at 41.6%. This means for all ages combined, less than half of the country’s population is seeking or already engaged in economically productive activities. LFPR is defined as the percentage of persons in the labour force (i.e. working or seeking or available for work) in the population.
Work Population Ratio and industry wise %age share of workforce
The work population ratio (WPR) in India still remains at 39.8% for July 2020 - June 2021. This means for all ages combined, less than half of the country’s population is actively engaged in economically productive activities. WPR is defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population.
Industry wise, around 1/3rd of the working population works in the trade hotel and restaurants sector in urban areas. For rural areas, agriculture remains the largest employer for both male and female workforce.
RURAL INDIA
URBAN INDIA
Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate in rural India is found to be much lower than in urban India for both male and female labour force. This busts the myths of urban folklore for jobs. The trend remains the same even when we consider the educated population with age 15 years and above.
All ages
In usual status (ps+ss) for educated (highest level of education secondary and above) persons of age 15 years and above in India
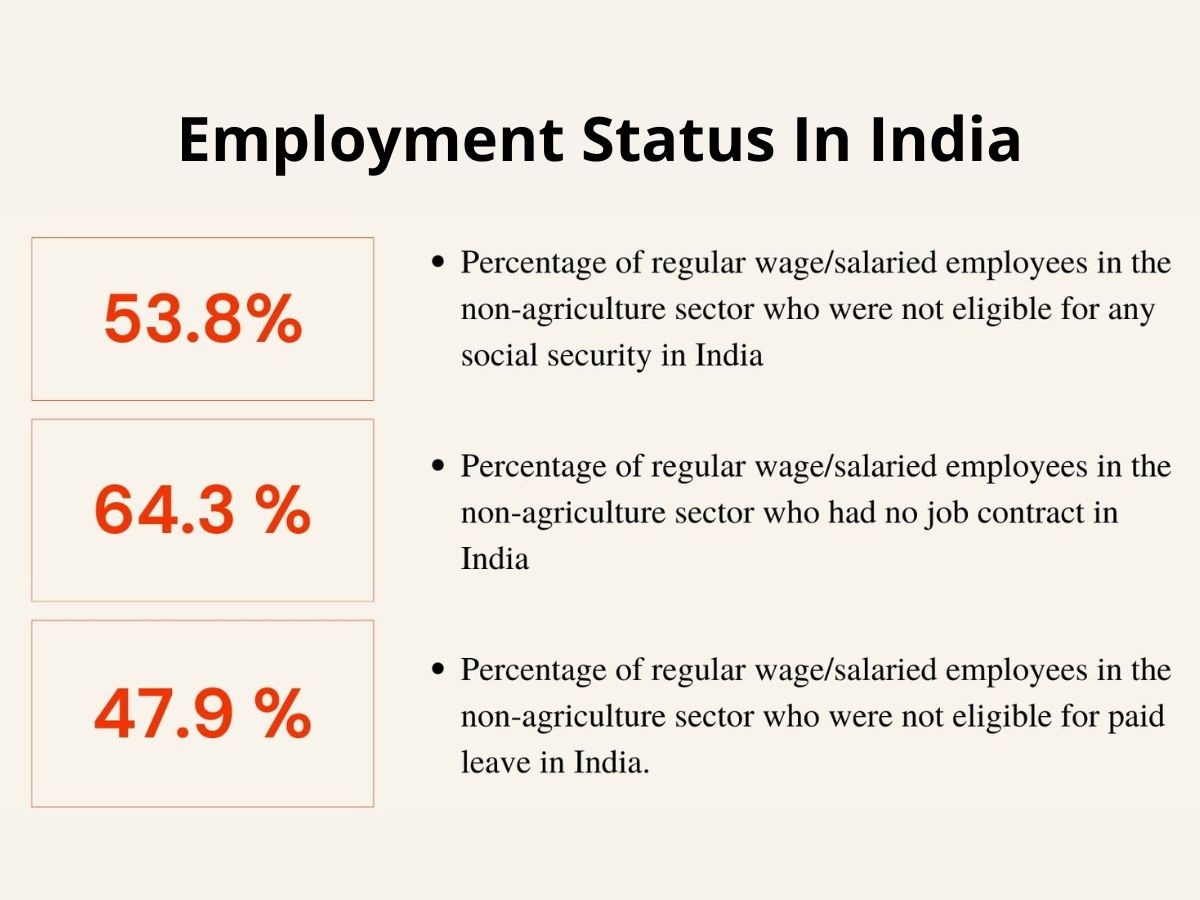
Some facts about the status of employment in India
%age of working force population engaged in the informal sector

No comments:
Post a Comment